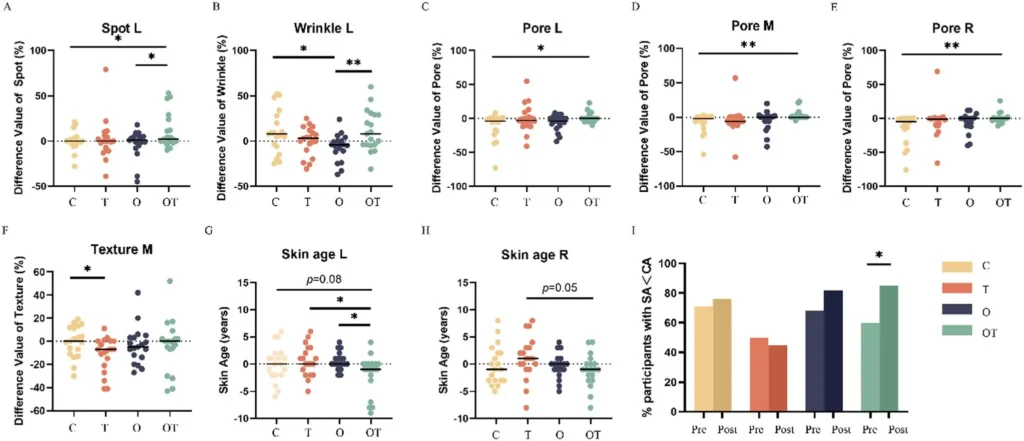
A recent study from Jiangnan University, published in the Journal of Food & Function, revealed the anti-aging potential of xylooligosaccharides (XOS). The study recruited 79 women aged 30-45 into four groups for an 8-week trial. The groups received either oral XOS, topical XOS, a combination of both oral and topical XOS, or a placebo. Results indicated that the combination of oral and topical XOS was the most effective, significantly improving various skin aging markers, including wrinkles, spots, and pores.
Key Insights from the Study Dual Intervention Impact:
The combination of oral and topical (OT) XOS treatment yielded the most significant improvements in skin rejuvenation and reduced facial pores. The OT group experienced a notable reduction in Cutibacterium, a bacteria associated with acne and pore issues, and an increase in beneficial gut bacteria like Bifidobacterium, enhancing the gut-skin axis effects.
Check and download the full study in PDF file here: Dual intervention on the gut and skin microbiota attenuates facial cutaneous aging
Microbiota Changes:
The OT intervention significantly increased skin microbiota diversity, reducing harmful bacteria and increasing beneficial ones such as Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia. Modifying skin and gut microbiota through dual interventions suggests that XOS can reduce bacterial growth associated with acne and other skin issues. Mechanistic Insights:
XOS works by inhibiting skin lipid synthesis and triglyceride production, which reduces sebum levels and acne. This effect is linked to a reduction in fructose phosphorylation and lipophilic Cutibacterium. Bifidobacterium also contributes to anti-inflammatory and oil-reducing effects by regulating tryptophan metabolism, making XOS an effective treatment for reducing pores and skin inflammation. Skin Improvement Metrics:
Skin age, measured using the VISIA system, was significantly reduced in the OT group, with participants showing younger skin than their actual age. Key skin aging markers, such as pores, wrinkles, and texture, showed marked improvements, particularly in the OT group. Additional Benefits of XOS In addition to its anti-aging effects, XOS offers a range of other benefits:
Moderate Sweetness: XOS is only 25% as sweet as sucrose, making it an ideal sugar substitute. Low-Calorie Content: Since the human body cannot digest XOS, it provides no calories, making it beneficial for blood sugar control. Broad Functional Properties: XOS has various bioactive benefits, including immune regulation, anti-inflammation, and antioxidant properties. Unique Flavor: XOS has a distinctive honey-like, slightly sour flavor. Natural and Widely Available: XOS is found in many foods and can be extracted from agricultural by-products. Future Implications While XOS offers numerous advantages, high doses may cause side effects like diarrhea and bloating, so it is recommended that daily intake not exceed 7.5 grams. Future research may explore safer and more effective ways to incorporate XOS into daily diets, potentially achieving the dual goals of enjoying desserts while staying youthful.
Conclusion This study highlights the promising role of XOS in modulating the gut-skin axis to improve skin health and combat aging. With its wide-ranging health benefits and potential as a prebiotic, XOS could become an essential component of anti-aging skincare routines. Additionally, its unique properties as a low-calorie sugar substitute suggest that future desserts could offer both taste and health benefits, making anti-aging more enjoyable and less of a challenge.

